The words yet and but are two of the most frequently used words in the English language. Many writers think these words are identical and can be used interchangeably. I am here to tell you that although these words are similar, they are NOT the same! In this post, we’ll teach you the difference between these coordinating conjunctions and demonstrate how to use yet & but in your writing!
What’s The Difference Between But vs Yet?
If you have been writing long enough, you have no doubt used these words in your writing. Just like the words nonetheless and nevertheless, they are easy to confuse! In fact, both words are most commonly used to introduce a contrast in a sentence. But do they do NOT have the same meaning.
“Yet” – Conjunction that is used to show that something has not happened or is not true up to this point. It is less certain and more mysterious than but.
For example:
- I haven’t finished my homework, yet I plan to get it done later. (He/she might finish it later.)
- She hasn’t arrived, yet I trust she’ll be here. (She might arrive later.)
“But” – Conjunction that introduced a contrast & treats it as 100% fact. There is more certainty than with the word yet.
For example:
- I want to go to the store, but I don’t have a car.
- She is tall, but she is not very heavy.
Takeaway: Both words (yet & but) are used to introduce a contrast. However, yet introduces a second clause that is less certain and more mysterious. Yet is also more formal.
When To Use Yet
As we already touched on, “yet” is a conjunction that is used to introduce a contrast or exception, just like the words incase vs in case. In most situations, it shows that the contrasting statement is less certain or is not true at this current time.
Here are some more examples of how to use yet correctly.
- Tom wants to be a pro basketball player, yet he never practices.
- Tina wants to pass her driving test, yet she has not studied.
The word yet is also frequently used at the end of sentences to achieve a similar mysterious effect. It is often used with negative sentences like “haven’t,” “isn’t,” “aren’t,” “hasn’t,” and “didn’t.”
- Tom hasn’t finished his homework yet.
- She hasn’t arrived yet.
- Mark hasn’t eaten lunch yet.
Just like we saw when analyzing the words doctor appointment or doctor’s appointment, spelling makes a huge difference! Adding one letter can change a phrase completely.
Using Yet In A Sentence
Here are 5 sentences demonstrating how to use yet in a sentence.
- I want to be president, yet I haven’t started campaigning.
- Steve wants to plat basketball, yet he hasn’t hit his growth spurt.
- Mark wants a job at the New York Times, yet he doesn’t write.
- Jesse wants to be a bank robber, yet he never robs banks.
- Brian wants to be an Engineer, yet he doesn’t like math.
Just like we saw in our post on nanna meaning, small spelling changes can totally change the meaning of the word or phrase.
When To Use But
Like we already mentioned, “but” is a conjunction that introduces a contrast. It is actually used very similarly to the terms other than vs other then in your writing. Unlike the word yet, but shows that the contrast is more certain. It assumes the contrasting phrase is fact without any emotion.
- I wanted to purchase a weapon, but California just banned the sale of weapons.
Unlike the word yet, but CAN’T be used as the last word in a sentence.
- [NOT CORRECT] She hasn’t eaten lunch but.
Using But In A Sentence
Here are a few sentences demonstrating how to properly use the word but.
- I wanted to go to the beach, but it was raining.
- She is usually very quiet, but today she would not stop talking.
- I had a lot of work to do, but I decided to take a day off instead.
- He is usually very punctual, but he was over fifteen minutes late today.
- I thought it was going to be cold outside, but it was actually 80 degrees out today!
Just like with the phrase “discussed about“, you need to pay close attention to the context of your sentence in order to get it right!
Explain Conjunctions
Now you know that the words but and yet are used as conjunctions in the English language. But what is a conjunction?
Generally speaking, conjunctions are words that join together sentences, phrases, or clauses. They introduce phrases just like the words “as well as“, but there are some key differences. There are three main types of conjunctions that we use regularly.
- Coordinating Conjunctions – Join words & phrases that are equally important. For example:
- I want to go to the store and buy some milk for my kids.
- She is tall but very thin.
- We can have pizza or Chinese food for dinner tomorrow night.
- Subordinating Conjunctions – Join dependent & independent clauses. For example:
- I will eat the cookie because I am very hungry.
- She went to the store since she needed milk for her children.
- Although it is cold outside, I am going for a walk for exercise.
- Correlative Conjunctions – Pairs of conjunctions that team up to join words or phrases together. For example:
- Both the cat and the dog are sleeping in their beds.
- You can either watch TV or read your book.
- Neither the cat nor the dog is awake right now.
Which Is More Popular?
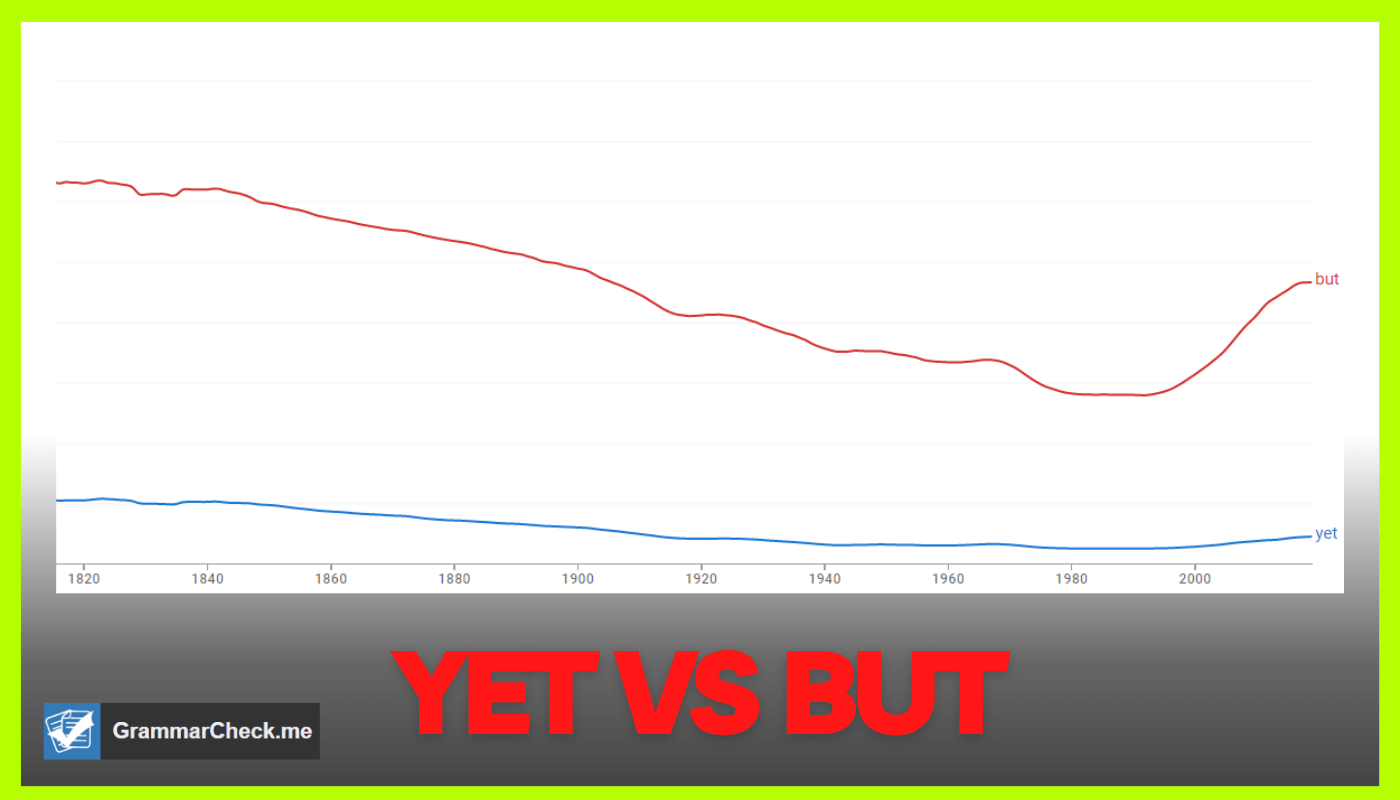
After reviewing Google’s ngram data, it is clear that the word but is used more frequently. Back in the 1800’s but was more popular in written literature. Then, in the late 1990’s it once again became more popular.
Just like we saw when comparing the words “in regard or in regards“, popularity of vocabulary changes over time. As culture changes, so does the way that people speak and write.
Frequently Asked Questions
It depends on the context of the sentence. If you are trying to introduce a contrasting statement that is fact, use but. Otherwise, use yet.
No, yet and but are different words with different meanings. You should not use them interchangeably.
Yes, you can use the two words but and yet to start a sentence. However, they should be used correctly as coordinating conjunctions.
You use the word yet to introduce contrasting statements that are not true at the present time but could be true at a later time. It can be used in both negative and positive sentences.
The Bottom Line
Now you are much more familiar with the coordinating conjunctions yet and but. Many writers use these words interchangeably without knowing they are slightly different words! Remember, yet is more formal and should be used in more formal works of writing. And if you need some extra help, use our FREE check grammar tool to make things easy!
