Can’t figure out the difference between a noun vs pronoun? Learn how to tell them apart in this article.
The three main components of a sentence that you should know are:
- Subject
- Verb
- Complement
The subject in a sentence will always be a noun, and sometimes it will be a pronoun. What’s the difference between the two parts of speech? You’ve come to the right place to find out.
This article will explain the difference between a noun vs pronoun to help you identify and use them in your writing. You’ll also have examples of nouns and pronouns in action.
What Is a Noun?
Let’s start with the basics and discuss what a noun is. After all, understanding what a noun is will be your basis for understanding pronouns.
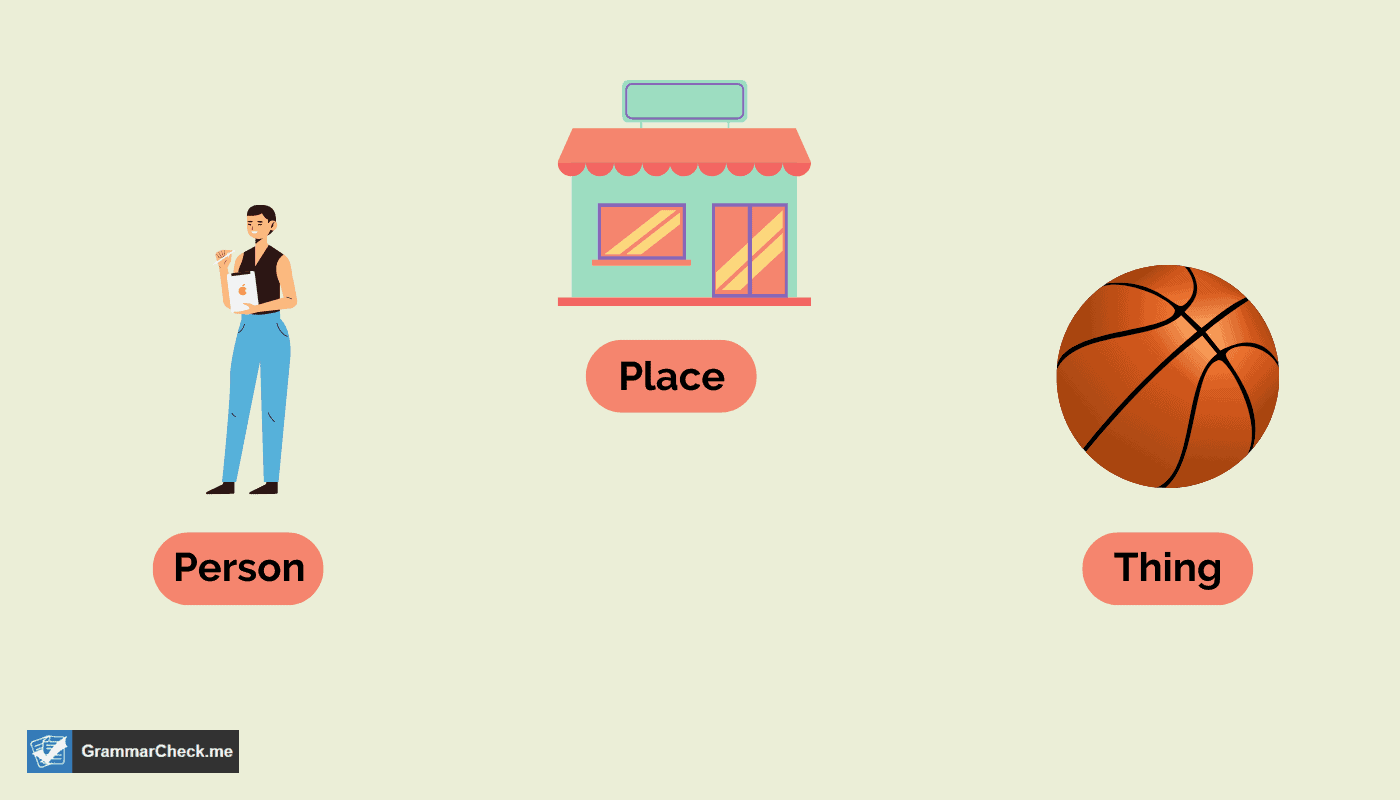
A noun, like ladle or ladel, is a word used to identify people, a place, or a thing.
There are several different types of nouns. Some types that you may encounter often include:
- Proper noun: a specific person, place, or thing
- Collective noun: a single noun used to describe a group of something
- Abstract nouns: an entity that cannot be perceived by the five senses, such as honesty or trust (opposite of a concrete noun)
- Predicate nouns – If you’re interested, check out what is a predicate noun example from our previous post.
Here are some examples of nouns:
- Book
- Beyonce
- Cat
- Oklahoma
- Love
Nouns, like Chris’ or Chris’s make up a large percentage of words in the English language, and you probably say a noun almost every time you speak. The presence of an apostrophe -S often indicates that it is a possessive noun!
One commonly used type of noun is a pronoun.

What Is a Pronoun?
A pronoun is a word that replaces another kind of noun in a sentence. The reason that we use pronouns is to avoid repetition and make writing and speech more coherent.
People often get tripped up using pronouns in their writing. For example, should they say Name and I or Name and me in my writing?
The most common type of pronoun is personal pronouns. There are three person pronouns in the English language:
- First-person: “I” (singular) or “we” (plural)
- Second-person: “You” (singular and plural)
- Third-person: “Him” (singular), “her” (singular), “it” (singular), and “they” (plural)
For example, you might say her Auntie or Aunty is a great woman! Other types of pronouns include:
- Demonstrative pronouns: introduces a question for a noun to answer (this, that, these, those, etc.)
- Possessive pronouns: referring to things that belong to someone (mine, your, his, hers, their, etc.)
- Indefinite pronouns: not referring to a specific person or thing (everybody, either, none, anywhere, somebody, etc.)
There are also reflexive pronouns, relative pronouns, interrogative pronouns, subject pronouns, and intensive pronouns. People confuse whether is it him and i or he and i in their writing!
The distinguishing feature of any pronouns is that the nouns or antecedents they are referencing have to be understood in the context. There are two main ways that you can ensure this:
- Mention the noun in the same sentence before the pronoun.
- Mention the noun in a prior sentence before the pronoun.
The standard rule here is that you cannot have a standalone pronoun if the context has not yet been established, and that context – the original noun – must be established or named before the pronoun is used.
Examples of Pronouns in a Sentence
To help you better understand how to use pronouns, here are examples of how different pronouns are used in a sentence.
Personal pronoun example
Personal pronouns usually refer to the speaker or the person or thing the speaker is referencing.
- Lucas was born in India, but he hasn’t been back since he was a baby.
- Mariah Carey is performing next week, her first performance in over a year.
- I saw a dog wandering the street this morning. It looked like a stray.
Demonstrative pronoun example
Since demonstrative verbs point to a specific thing, you’ll usually use them in speech and conversation, where you can physically refer to the subject.
- This is my favorite book.
- I’m not sure what that is, but it sounds complicated.
- These are yours, make sure you don’t forget them.
Possessive pronoun example
Possessive pronouns are used to express ownership. Often with these pronouns, context is vital to ensure a thorough understanding.
- That glass belongs to him, and this one is mine. (Note that “this” in this sentence functions as a demonstrative pronoun)
- I met her Mama or Momma last weekend.
- I’m not sure which of these coats is yours.
- My phone isn’t working. Can I use yours?
Indefinite pronoun examples
An indefinite pronoun doesn’t specifically identify what they’re referring to.
- The neighbors said someone broke into their garage last night.
- We tried everything to fix the problem, but nothing worked.
- Most people eat dinner before 8 pm, but others prefer to eat later.
Although you’re now equipped with new knowledge of nouns and pronouns, you might still be wondering what the difference between the two is. Let’s find out.
Noun vs Pronoun: What’s the Difference?
Generally, it doesn’t make sense to pit nouns and pronouns against each other, as every pronoun is a noun, but not every noun is a pronoun.
That said, there’s one general rule that differentiates nouns from pronouns. You can replace a pronoun with another noun. You can’t say the same for every type of noun.
Here are a few other differences between nouns in general and pronouns:
- You can pluralize nouns without making a sentence sound confusing, while pronouns you cannot.
- Nouns can be preceded by the articles “the” or “a.”
- An adjective can precede a noun.
These three general rules will help you differentiate nouns from pronouns better and understand when to use each.
The Takeaway
Understanding the difference between a noun vs pronoun may seem difficult at first, but the difference becomes clear with regular use of the two.
While all pronouns fit under the umbrella category of nouns, pronouns have different characteristics from other types of nouns. Once you wrap your head around the differences, using pronouns and nouns becomes a breeze.
